Polypropylene (pp)
Hits : 1409 |
What is polypropylene (PP)?
Applications of polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a type of proolefin that is a little harder than polyethylene. Polypropylene is a commodity plastic with low density and resistant to high heat. PP has a high melting point, durability and high load bearing capacity.
Its compound can be used instead of polypropylene (PP). The difference between compound and masterbatch is in their application, in such a way that compound is used to produce the final product, but masterbatch gives special properties to polymer raw materials.
Application of polypropylene (PP)
Among the applications of polypropylene are its use in packaging, automotive, consumer goods, medicine and cast films, and its chemical formula is (C3H6)n. It is also used in blow molding, injection molding, textiles and pipe production. After the passage of time and decay of products produced with PP polymer, they can be converted into polypropylene flakets and reused in the manufacture of new products.
Polypropylene and polyethylene have similarities in appearance and physical properties, but they are completely different in terms of application, production process, and chemical structure. The important differences between these two materials have been fully and partially addressed.

Polypropylene (PP) is divided into two categories: polypropylene homopolymer and copolymer. In the following, they have been examined:
Polypropylene homopolymer
They are thermoplastic resins that are produced through the polymerization of propylene with Ziegler-Natta catalysts. Homopolymers can be used in various processing technologies such as injection molding, blow molding, film, fiber, sheet extrusion and thermal forming.
In addition to the above applications, PPH homopolymer polypropylene has features such as higher strength-to-weight ratio, longer durability, and greater material stiffness compared to polypropylene copolymer, and for applications that require good resistance to impact, corrosion, and chemicals. It needs good weldability and processability.
"Z 30 s"
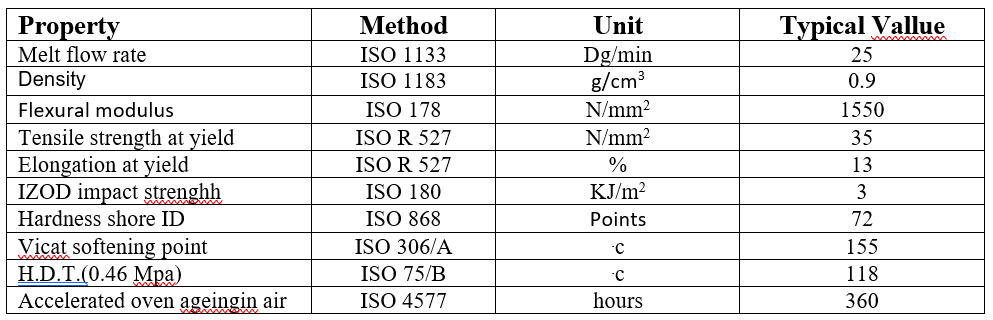
Polypropylene copolymer
Copolymers have a second monomer of ethylene, which increases the impact strength compared to polypropylene homopolymer. The key properties of polypropylene copolymer are high impact strength, good chemical resistance, better resistance to cracking at low temperatures and increased flexibility.
Polypropylene copolymer can be used in cases such as making car parts, containers, packaging and family products. It is also widely used in injection molding for various parts and medical devices.
"Moplen EPD60R"
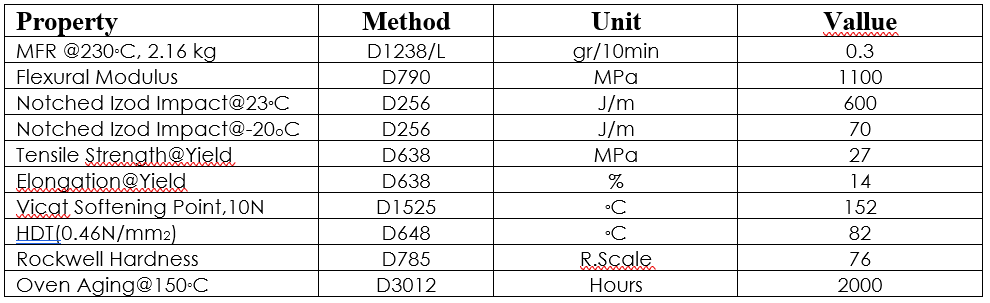
Polypropylene (PP) is a lightweight, hard, rigid, and crystalline thermoplastic that comes in a variety of forms. Among the advantages of polypropylene are its melting point, density, chemical resistance, and flammability. Polypropylene is also available in compound form, which is important in determining the quality of a compound from the poor quality in the final product.
Features of Polypropylene (PP)
Lightweight and strong
It is light in weight and also has good tensile and bending strength.
Chemical resistance
It has high resistance to corrosive substances such as acids and solvents and can be used to make corrosion-resistant parts.
Heat resistance
It has high resistance to temperatures up to about 130 degrees Celsius and has a high melting point.
Electrical insulation
Due to its insulating properties, it can be used to make electrical parts and electrical coatings.
For more information, you can contact us through our address and contact number.
Related posts:
?What are polymer raw materials/www.wci-polimer.com
What is polyethylene?/www.wci-polimer.com
© 2026 wci-polymer.com All Rights Reserved.


